We all like to enjoy music in our house or at a show with our friends. Still, unless you have an expensive Bluetooth speaker or you are driving in your car, it’s hard to enjoy music while you are out in the world. What if you want to go out to the park and have a picnic with your date and listen to music together? This is hard to do with our small and weak speakers that come standard with our phones. The solution to this would be to make something that makes our crappy speakers on our phones less crappy and louder.
While this can be achieved a number of ways — you could build an amp using electronic components or even program a Raspberry Pi to boost the signal — all these things require power. I am looking for a simple way to make my phone louder without worrying about power or price.
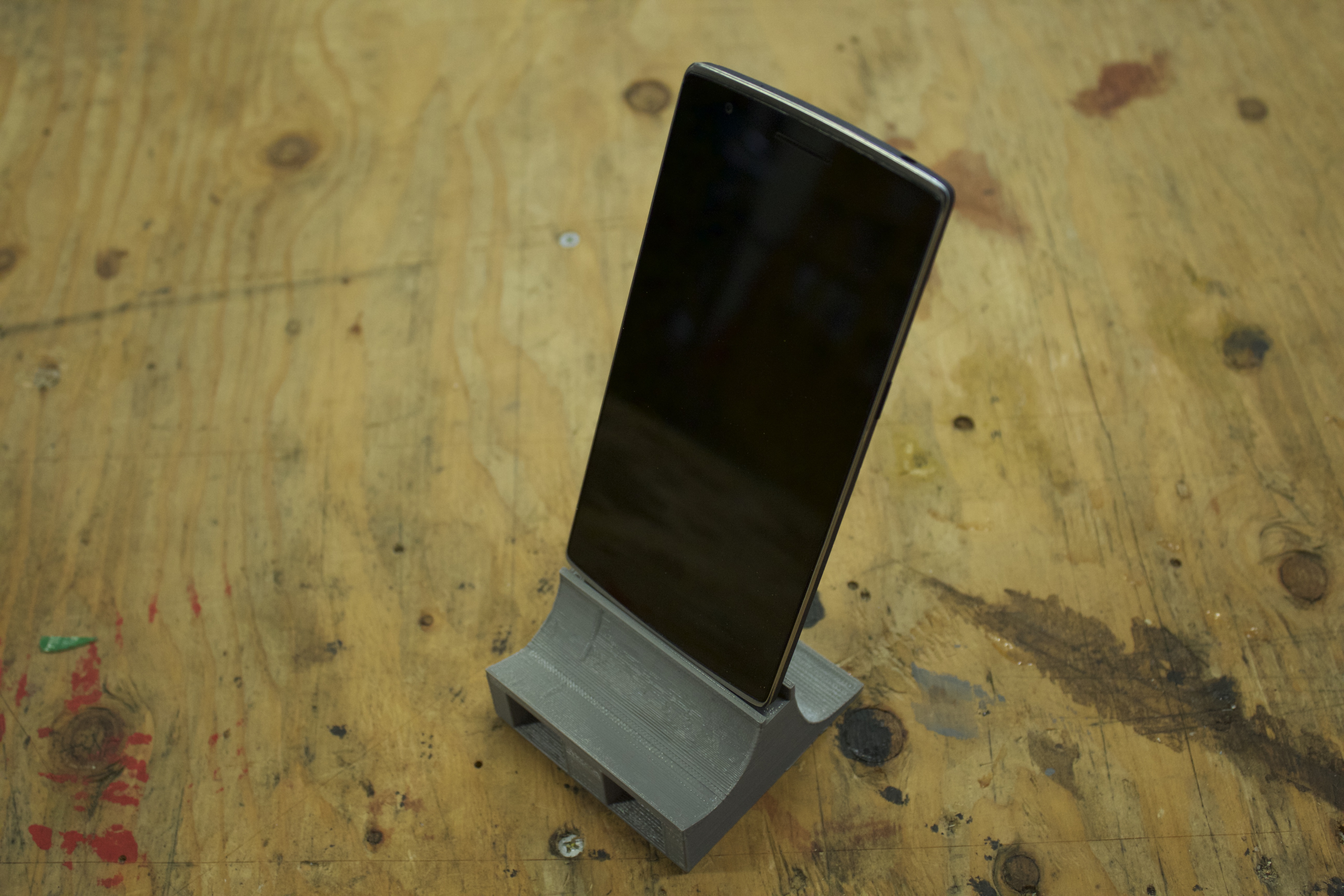
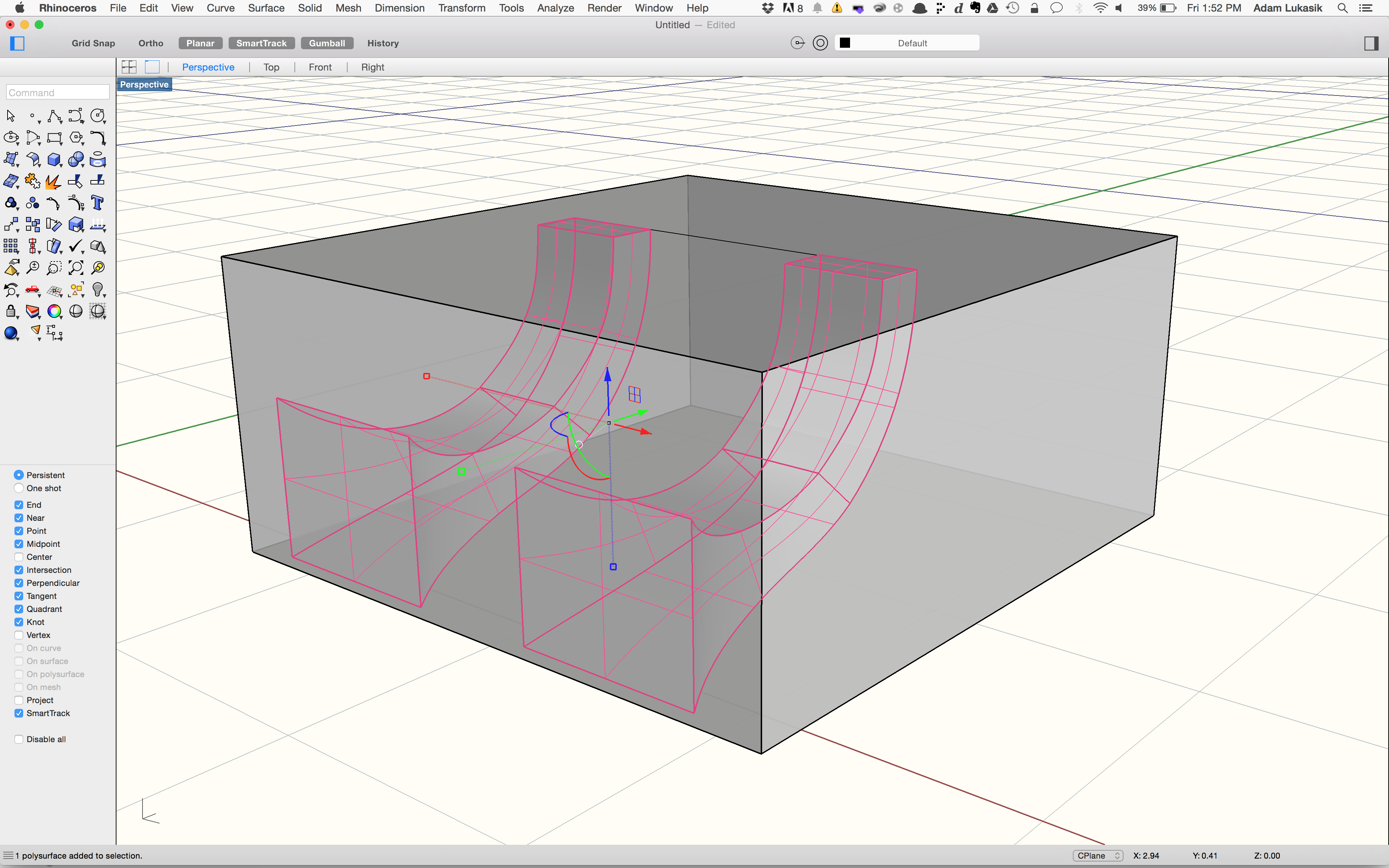
The best way to do this is to design and build a passive speaker for your phone. A passive speaker is an amplifier that magnifies the sound of your phone’s inbuilt speaker using the properties of sound and physics. In fact most modern speakers use the basic principles to help them amplify the sound they produce. The back of modern speakers is an empty chamber where the sound is allowed to echo and then escape to increase the sound. While this may seem like a strange way to add volume, it is not only the cheapest option, but if a designer has an in-depth understanding of sound physics and materials, they can dramatically increase the volume and sound quality of the speakers.
Using the basic principle of a loudspeaker and its geometry, we will explore how to design this type of speaker for your phone and print it on a 3D printer.