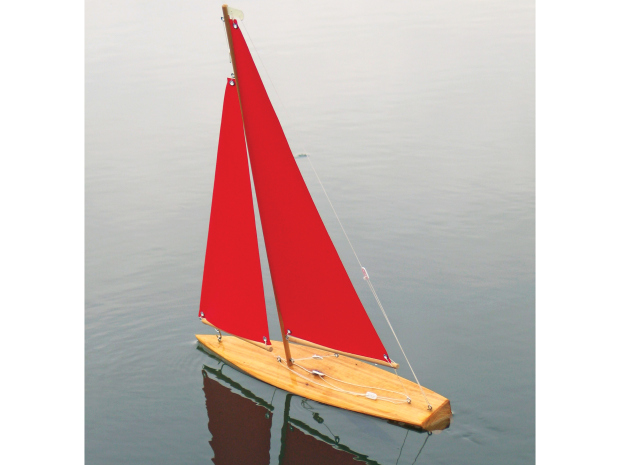
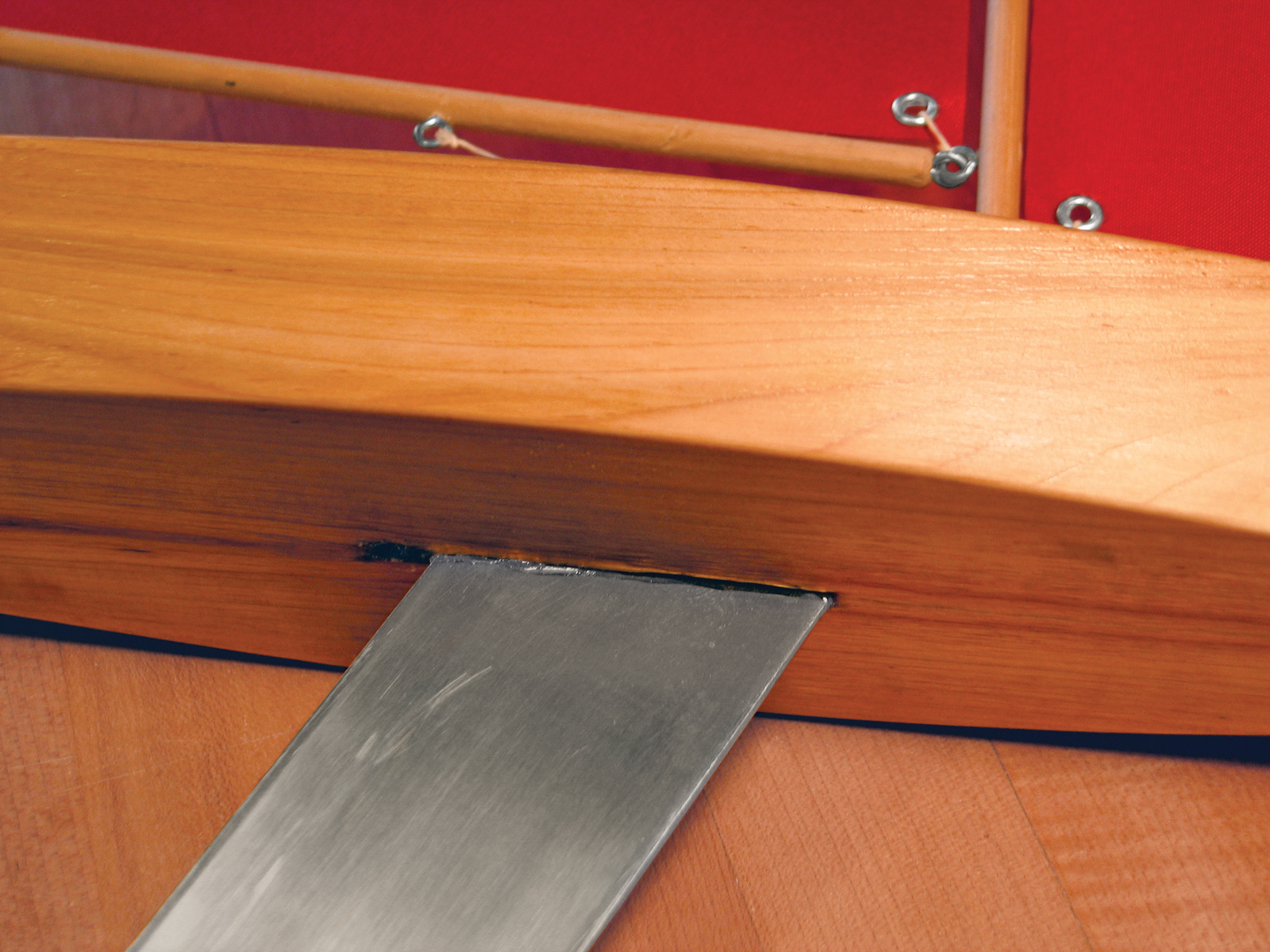
After the sail material is dry, trace and cut it to the plan patterns. Lay the boat on its side on a hard surface with the masts and booms in place and fit the sails to the areas for rigging. For the grommets, cut a small X at each sail corner, insert a grommet up through the hole, press the cloth down around it, and tap the grommet flat with the eyelet tool until it firmly grips the cloth.
NOTE: It’s a good idea to practice setting grommets first with a couple of sailcloth scraps and extra grommets. It’s time for rigging. Knot and cut a short length of dacron line, thread it through a bowser, and string the boom vang. For these and all other knots, add a tiny drop of cyanoacrylate glue immediately after tying; the line is slippery and won’t hold knots otherwise.
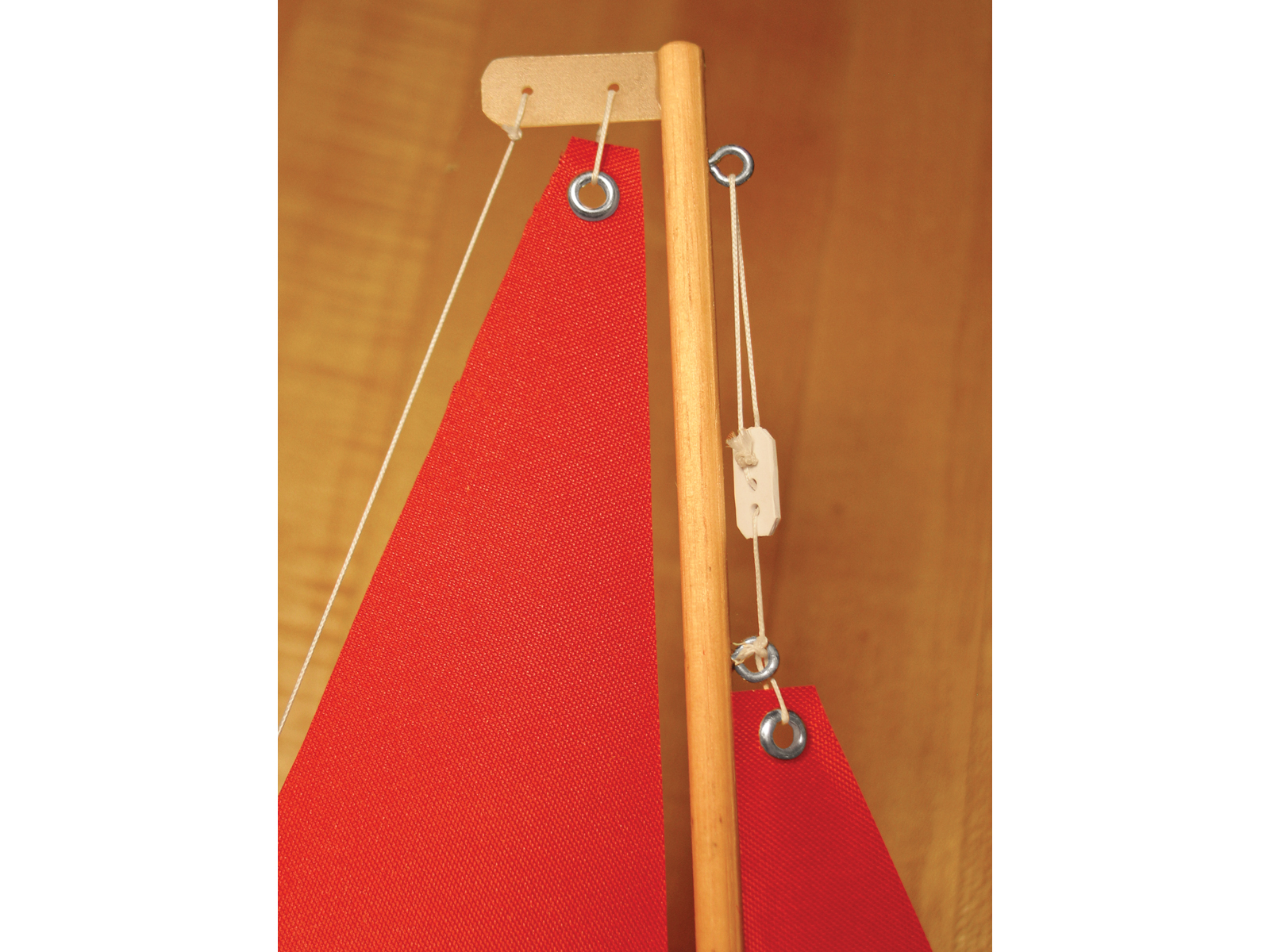
Use 5″ lengths of line to tie each sail grommet to its corresponding screw eyelet or drilled hole with a square knot. You’ll need about 10″ for the top of the jib sail, which threads through 2 eyelets before tying off to the uphaul bowser.
Referring to the plans, tie the 4 lower connections on the booms first, and then add the upper lines for tension, so there are no wrinkles in the sails along the booms. Thread a bowser onto the jib uphaul as indicated: for their final tensions, you’ll adjust the jib using the uphaul at the top, and the mainsail using the boom vang.
For the backstay, tie in a long length of line at the masthead crane and install a bowser, routing the line through the eyelet at the stern.
Tighten the backstay and the sails so that they’re fairly tight but the mast is not bowed forward or aft. Finally, add the 2 lines called sheets. For these, cut two 15″ lines. Tie each one through the hole in the aft end of a boom, thread it through the sheet eyelet on the deck just underneath, then through 2 holes in a bowser, through the other sheet’s eyelet, and finally through the last hole in the bowser, doubleknotting the line.
NOTE: It’s important to tie the bowsers exactly as shown on the plan to make them work. The sheets let you adjust the angle (trim) of the sails — slack for downwind sailing or tight for crosswind — letting you cross a pond or pool in any direction that isn’t too close to directly upwind.