
Yesterday, I posted a reprinted from my old tech site, Street Tech, of a piece I did on Zach DeBord’s solar-powered vibrobots. Here’s another piece from Street Tech, one on building solarrollers, a simple kind of solar-powered car common in beginner BEAM robotics. Like the vibrobots, this would make a perfect project for a family who’s just learned how to solder and wants to collaborate to build something fun (and cool!). – Gareth

Gopod bless Flickr! While searching on it recently to see if anyone else had built Mousey the Junkbot or a Symet or Solarroller inspired by my BEAM robotics articles in MAKE, Volume 06, I discovered Zach DeBord and his amazing BEAM creations. A Chicago-based designer and Web developer who’s done work for (among others) Comcast, Volvo, and Yellow Tail (mmm…wine), Zach’s bots put the “A” (“Aesthetics”) back into BEAM, with gorgeous, meticulously-rendered designs that are as much objets d’art as autonomous robo-critters.

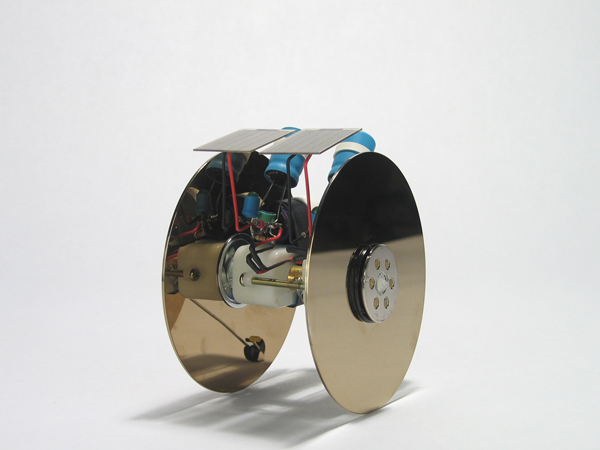
All of his robots are awesome-looking, but I was instantly attracted to this roller because it’s bigger than any solarroller I’ve ever seen, and it uses two solar cells, four storage capacitors, and two gearmotors. Ingeniously, this roller can be steered (sorta). Zach writes: “It is currently configured to go forwards, but by angling either solar panel, it will turn more in one direction since one panel will be getting more light. With both panels angled in the same direction, it is pretty phototropic.”
The two large drive wheels on the roller where made from the discs found in old SyQuest 270MB 3.5″ removable cartridges. Of these, Zach sez: “The SyQuest platters make great wheels except that they’re fairly slick. I plan on getting some rubberizing paint and putting beads along the edges to give the wheels more traction.” The third wheel, an idler, “keeps the motors from dragging on the ground. It is actually a small plastic part also taken out of the SyQuest disc.”

For this design, Zach used two FLED-based voltage-triggered Solar Engines (Type 1). In my “Beginner’s Guide to BEAM” and the “Two BEAMBots” projects in MAKE, Volume 06, we also discussed and used voltage-triggered Type 1 SEs, but they used a 1381 voltage detector IC to control the circuit. FLED-based SEs use a Flashing LED (hence “FLED”) in place of the 1381. On the FLED SE page in the Circuits Library on Solarbotics.net, this is how BEAM guru Wilf Rigter describes the way in which such a circuit works:
“The solar cell charges the main capacitor until the voltage is high enough for the FLED to start flashing. When the FLED flashes, current flows through the FLED and the base of the PNP transistor and it turns on. Now current passes through the PNP into the base of the NPN transistor and it turns on. When the NPN turns on the collector which is connected to the motor and the 2.2K resistor goes low (to GND). This places a voltage across the 2.2K resistor which provides more base current for the PNP transistor which makes it turn on even more. That is called positive feedback or latching of the circuit because both the PNP and NPN transistors remain on until the main capacitor is discharged to less than 0.7V. When the capacitor voltage drops below 0.7V the PNP and NPN transistors both turn off because of the minimum voltage required to keep the base emitter turned on.”
Here is a schematic for the basic FLED SE circuit, taken from Beam-Online.

Zach on building BEAM Roller circuits: “I usually build engines in a batch for later use. In the image below, you can see that there are sockets on top of the engine circuits (made from IC socket pins). These are used to easily plug in the solar cells. The two leads (red and black) coming out of the back of the engines go to the motors. In this picture you can see the two types of engines that I make: one “classic” configuration with storage capacitors (the two engines on the left) and another config using Polyacene disk batteries in place of the caps (which deliver roughly .6 Farads of stored power). These are represented by the three engines on the right.”

Parts List
Here is a list of the parts that Zach used to build his bot. Solarbotics parts numbers are given, but you can also get many of these parts from your own techno-junk collection, from Radio Shack, or other electronics sources.
| Quantity | Part | Solarbotics Parts # | Notes |
| SyQuest Disc Platters | N/A | Dumpster diving, anyone? | |
| 3v Solar Cells | #SC2433 | Any 3v cells, such as the 24mm x 33mm ones SB sells. | |
| Gear Motor GM3 | #GM3 | These are 224:1 90-degree shaft motors | |
| 2200uF caps | N/A | N/A | |
| 4700uF caps | #CP4700uF | N/A | |
| 2N3904 NPN transistors | #TR3904 | N/A | |
| 2N3906 PNP transistors | #TR3906 | N/A | |
| Flashing LEDs | #FLED | N/A | |
| 2.2K-ohm resistors | #R2.2k | N/A | |
| IC Socket pins | #SPin24 | These are on a 24-pin DIP that you pull off to use. | |
| 1/2″ piece of 1/4″ tube | N/A | Used as a spacer between engines. | |
| 1.5″ screw | N/A | To fasten engines together (via hole on motor casings. You just need to find a screw that’ll fit snuggly. | |
| Round plastic piece | N/A | To be used as back stabilizing wheel. Zach got his from the same SyQuest disc. | |
| Heat Shrink Tubing | N/A | Radio Shack has an assortment in various sizes. You’ll want it all the way up to 2″ dia. | |
| Heavy Duty “Jumbo” Paper Clip | N/A | N/A | |
| Hook-up Wire | N/A | Use red and black to keep things colorful and polarity-coded. |

Zach’s twin-engine roller next to a more common single-engine variety.
In the Maker Shed:
SolarSpeeder Kit
The SolarSpeeder was designed with ideas gathered from many years of Solarroller racing at the BEAM Robot games. You only need a soldering iron and basic hand tools to turn this high-quality coreless DC motor, lightweight body, and tweaked electronics into your own solar speed-demon.
2 thoughts on “How-To: Build a BEAM solarroller”
Comments are closed.
ADVERTISEMENT
Join Make: Community Today









I don’t know what the policy is for posting a link to someone who’s selling stuff, so if I cross the line I won’t be offended if this gets deleted.
This guy is selling super caps for cheap. Check out the 2.7V/20F capacitor:
http://stores.shop.ebay.com/Electronics-Salon_Double-Layer-Capacitors_W0QQ_fsubZ272708919QQ_sidZ804830199QQ_trksidZp4634Q2ec0Q2em322