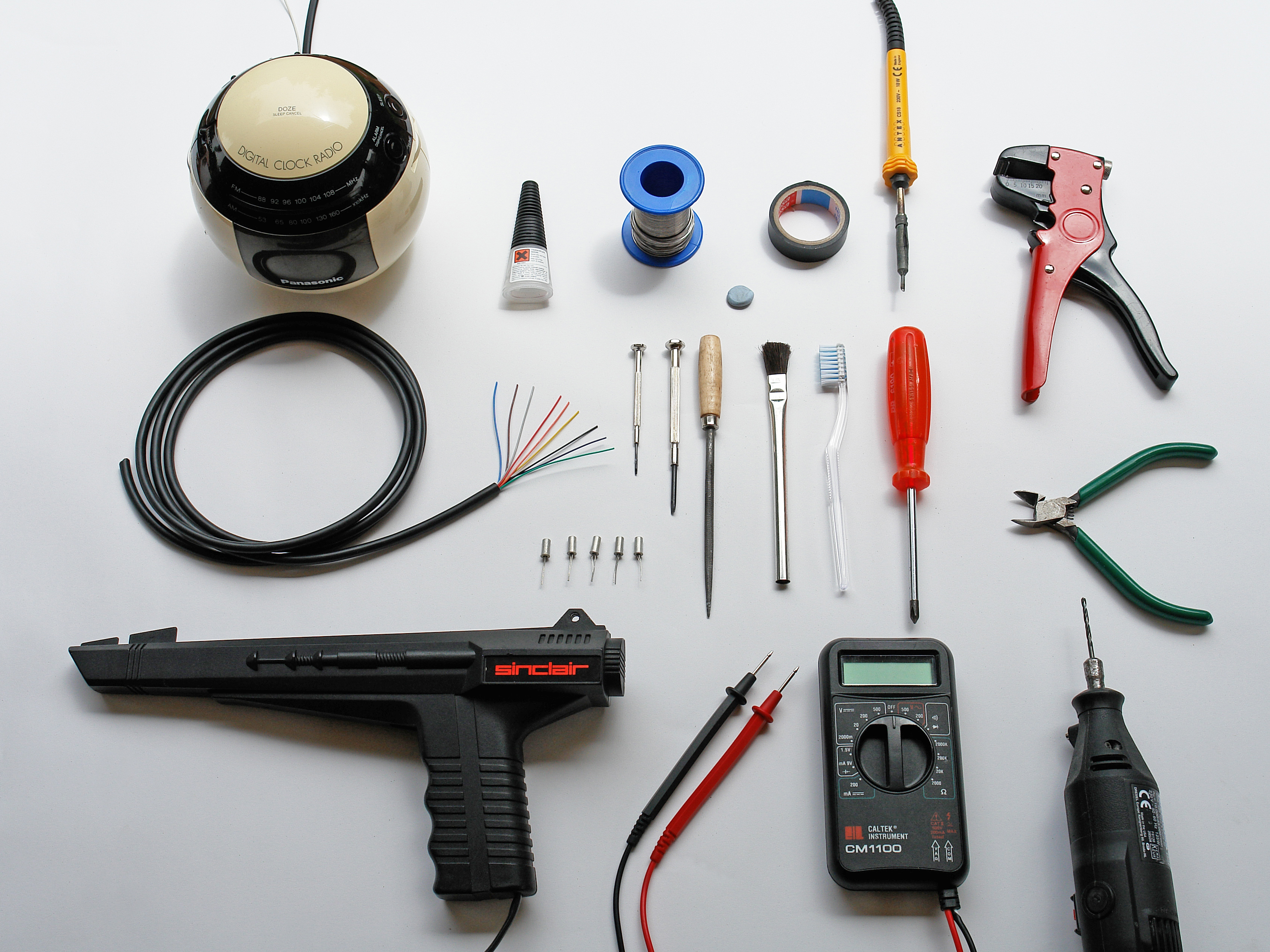
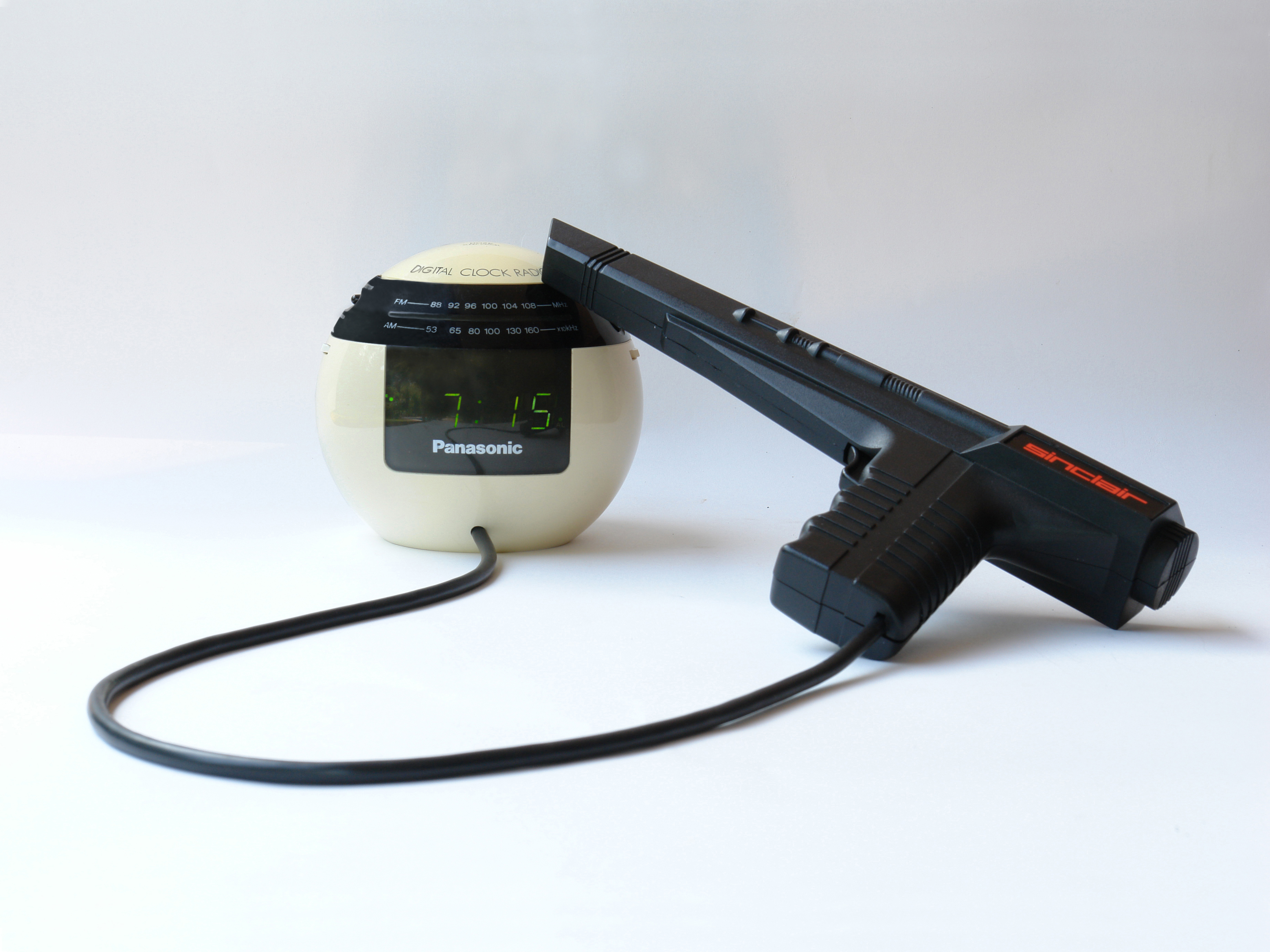
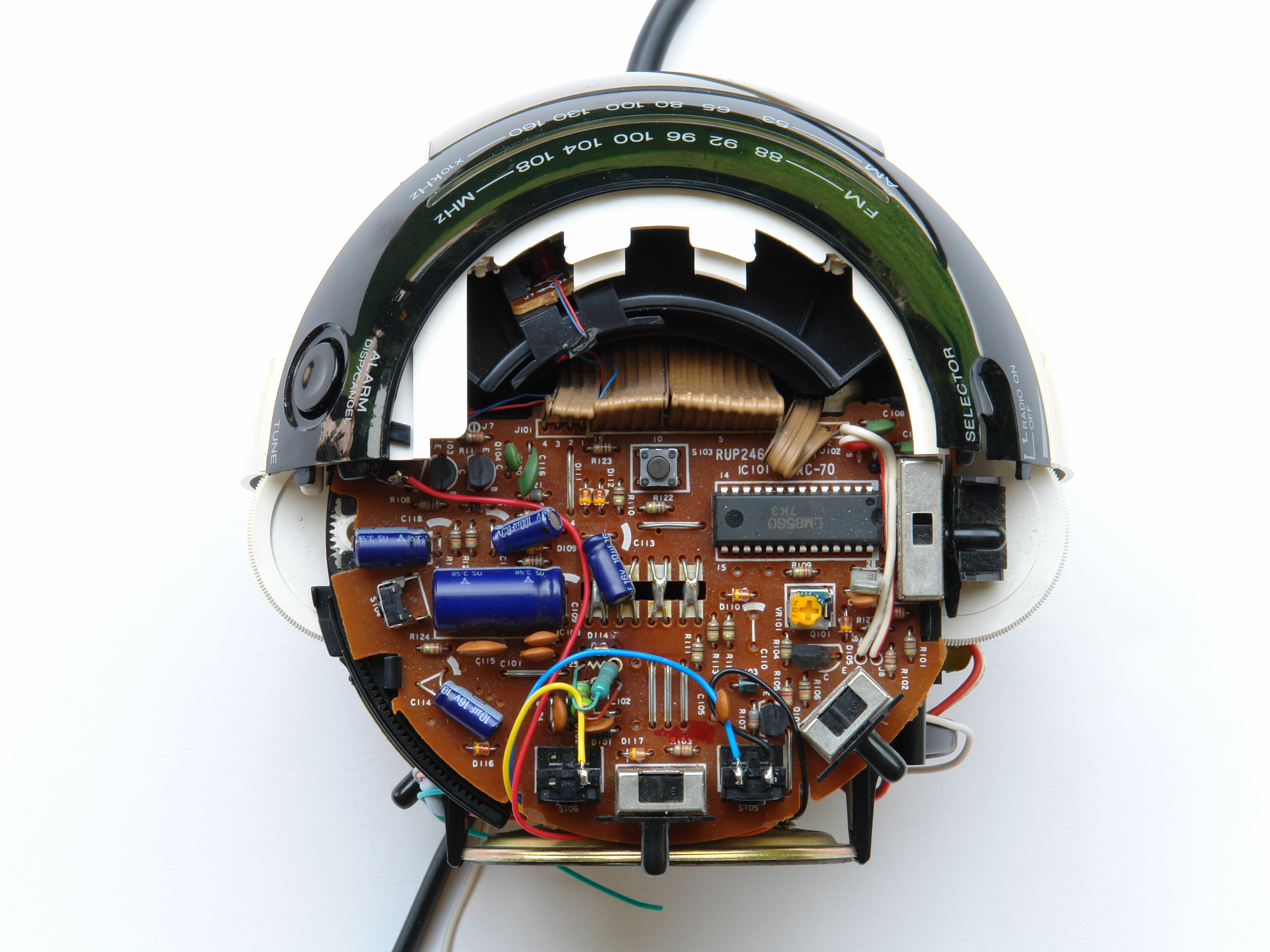
If you aren’t modding a Panasonic RC-70, don’t worry, because almost 99% of digital clocks work the same way. Just remember that each button has 2 connections, which come into contact with each other when you press the button. You want to extend these connections so that, instead of closing the circuit with the button, you’ll be using the light gun.
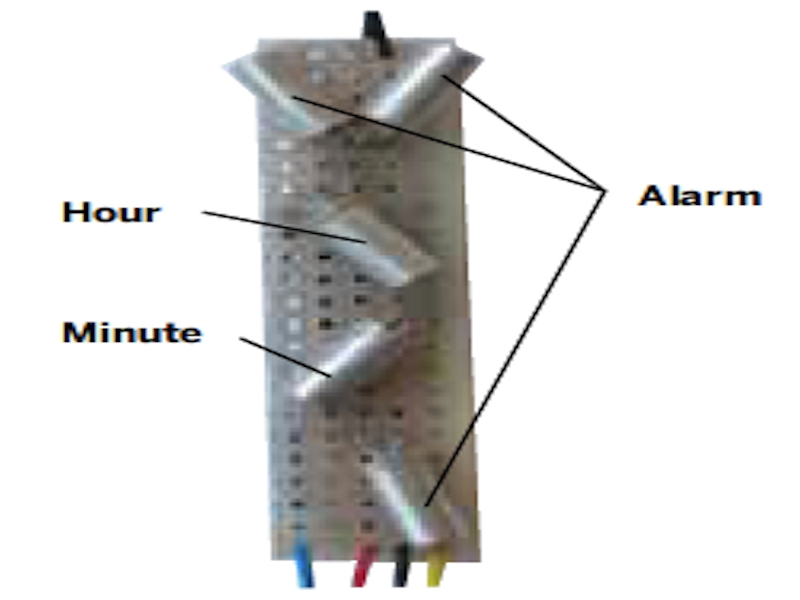
Find the buttons that control the essential functions: set time and alarm (hours and minutes), and alarm off. The RC-70 uses just 3 buttons for these: Alarm, Hour, and Minute. The Alarm button does double duty, shutting off the alarm and switching the Hour and Minute buttons from “time-set mode” (the default) to “alarm-set.” Some clock radios use a switch instead of a button to change between time-set and alarm-set modes.
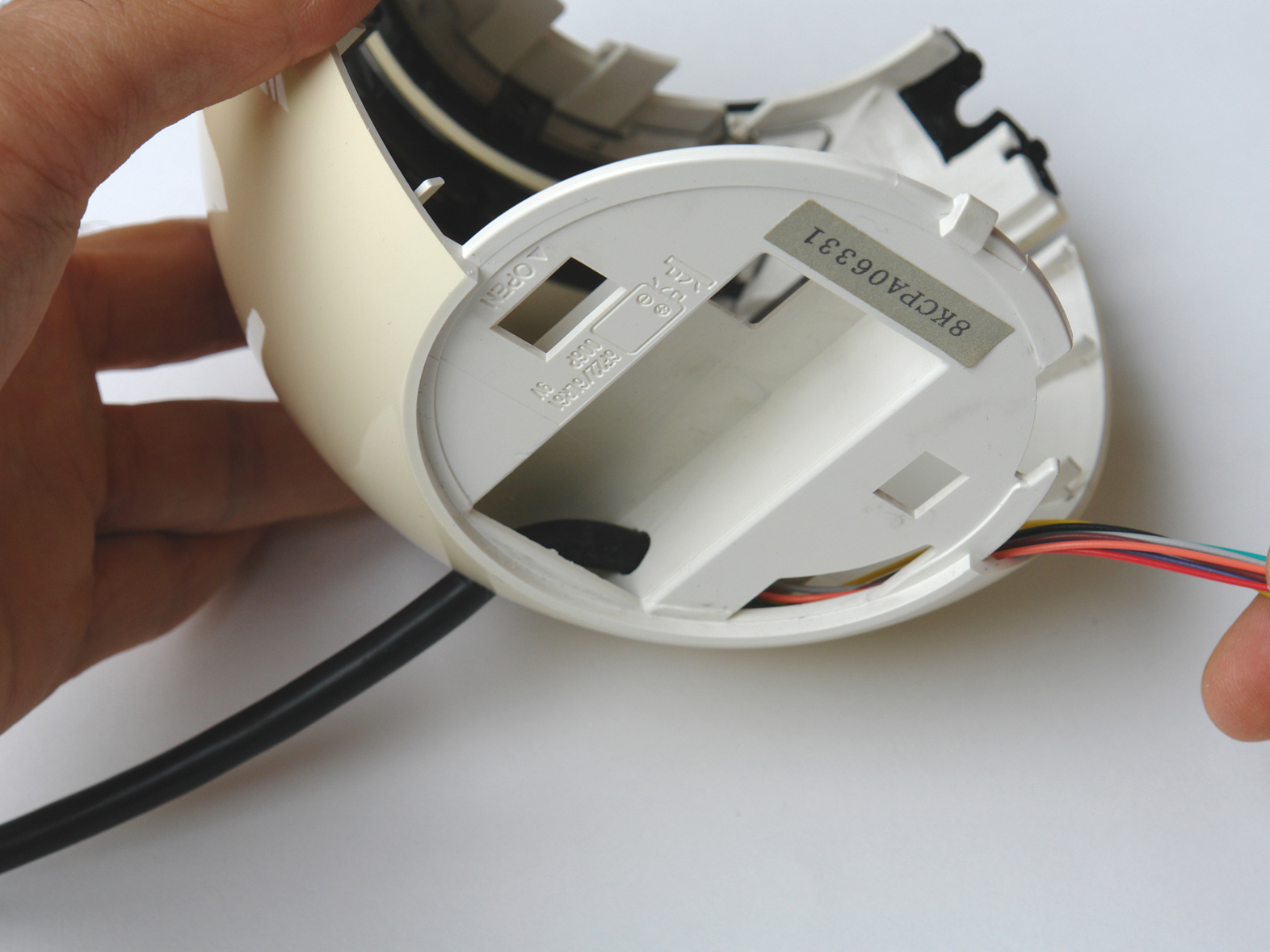
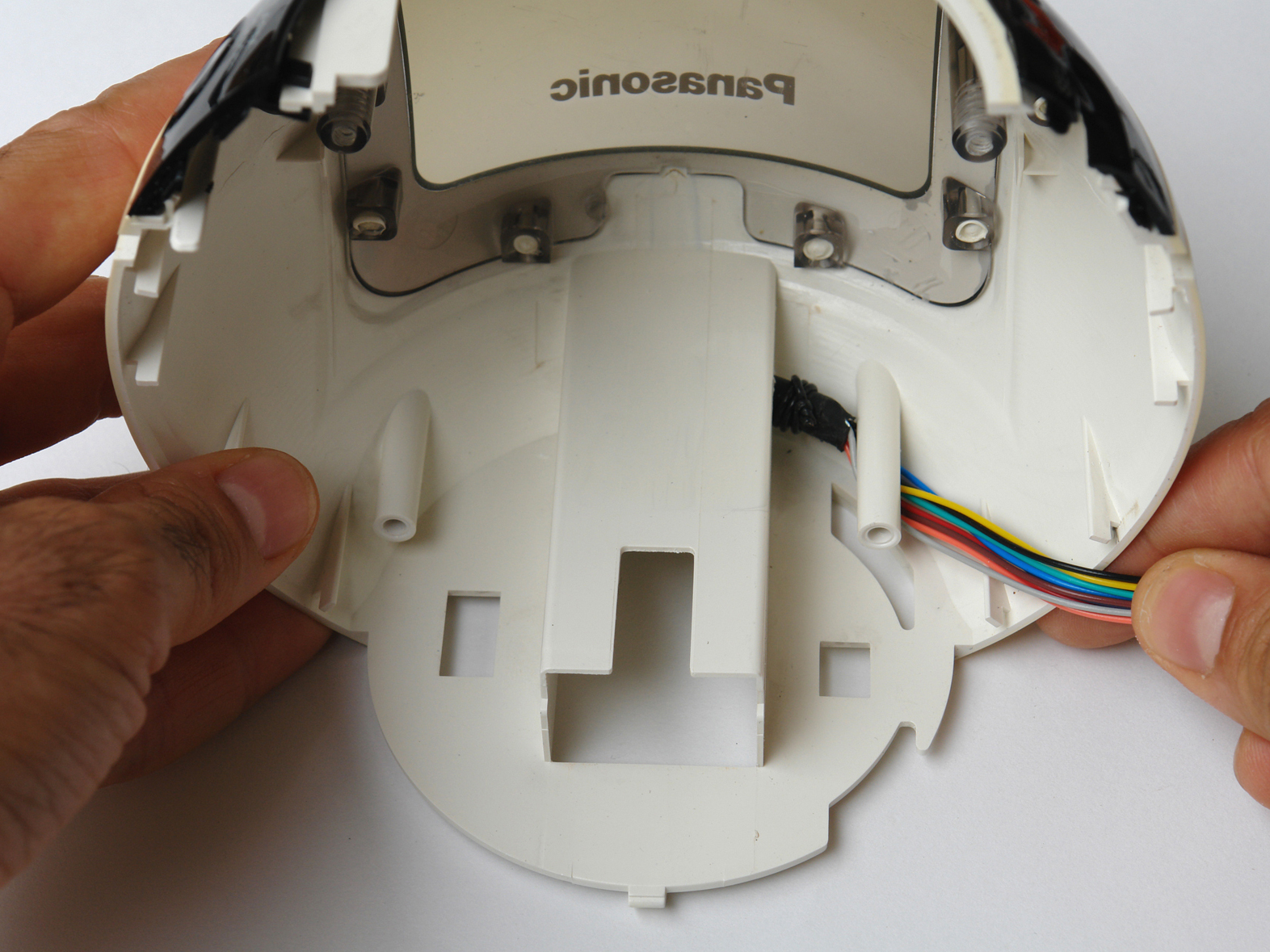
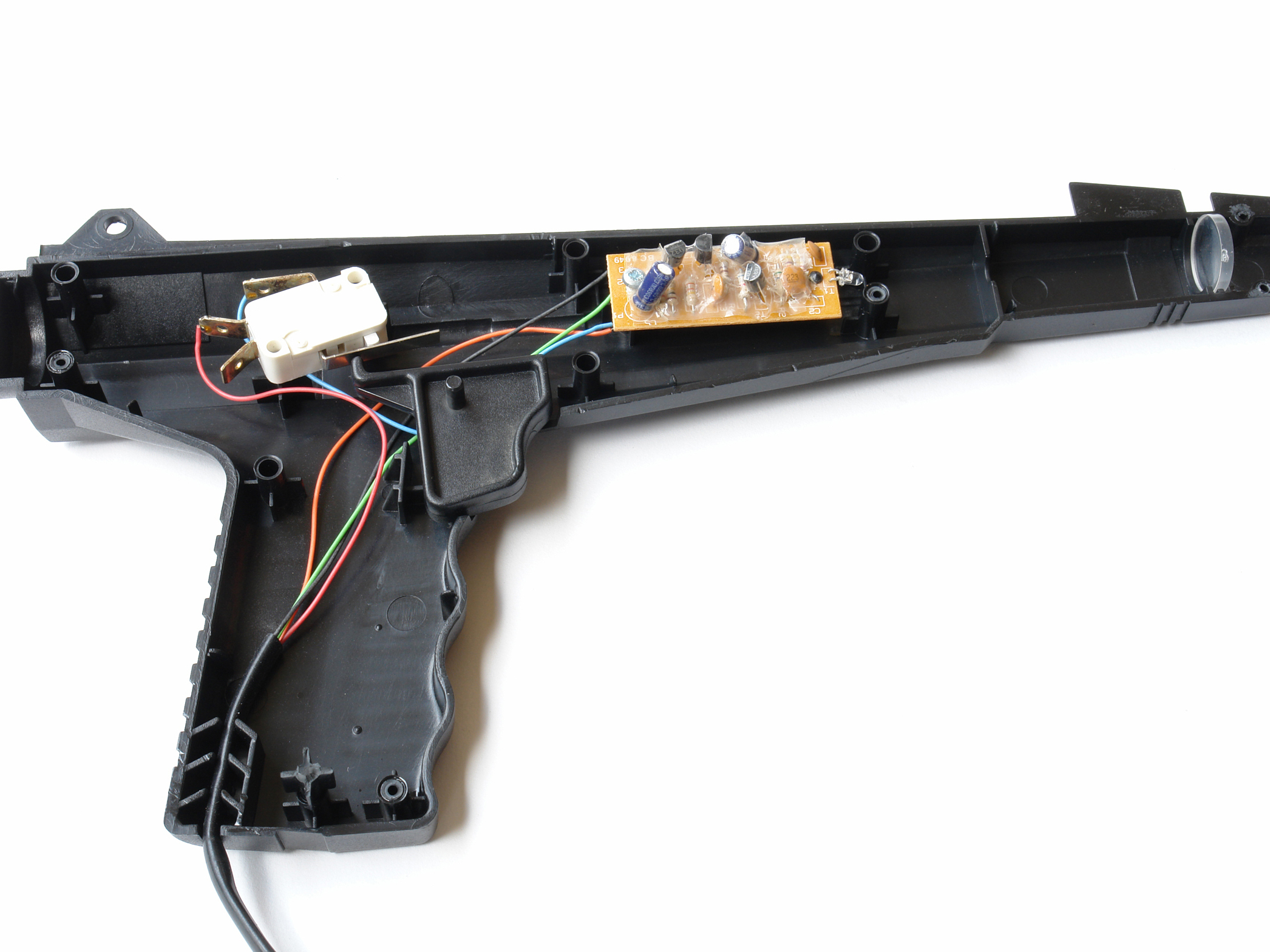
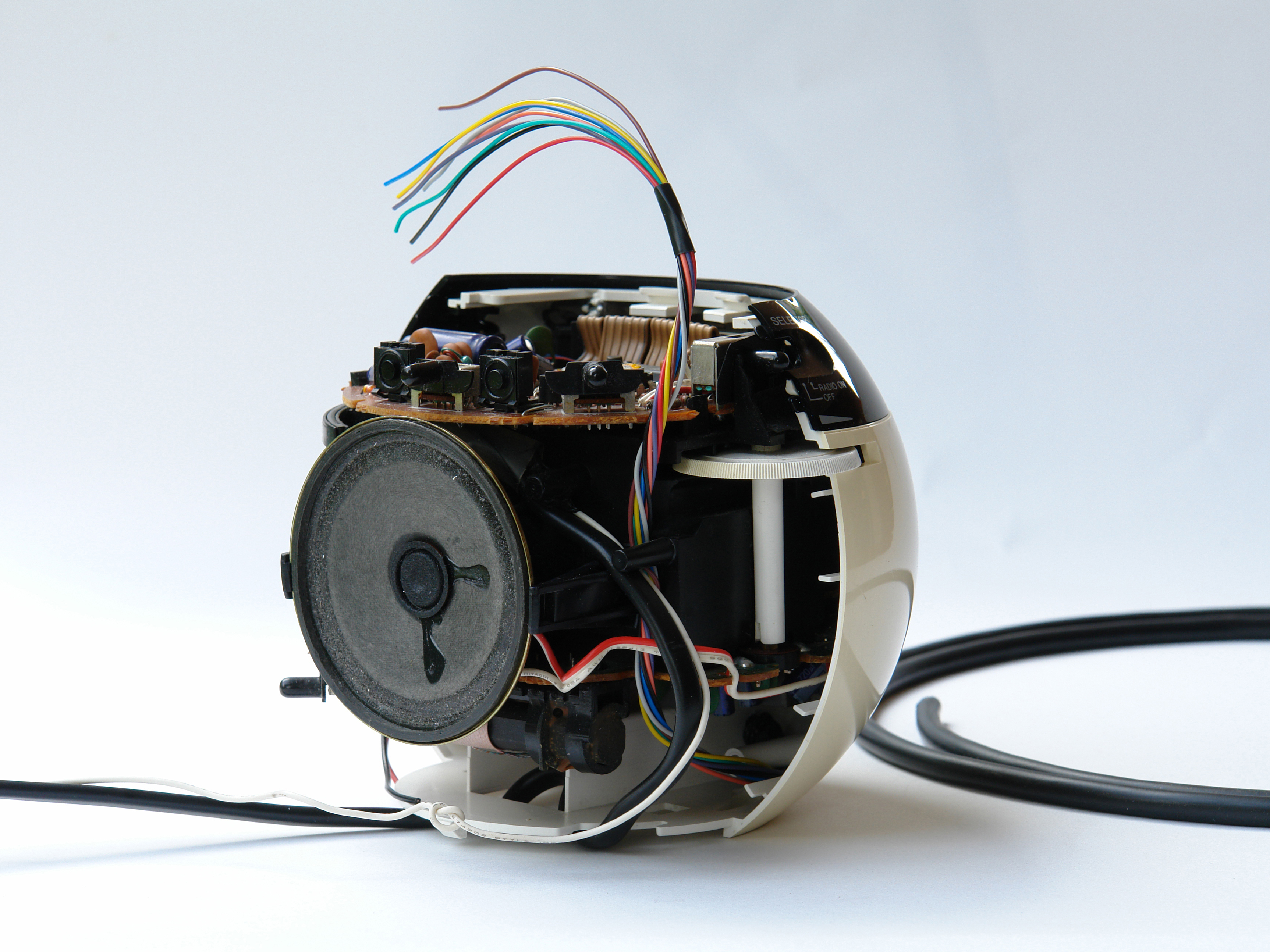
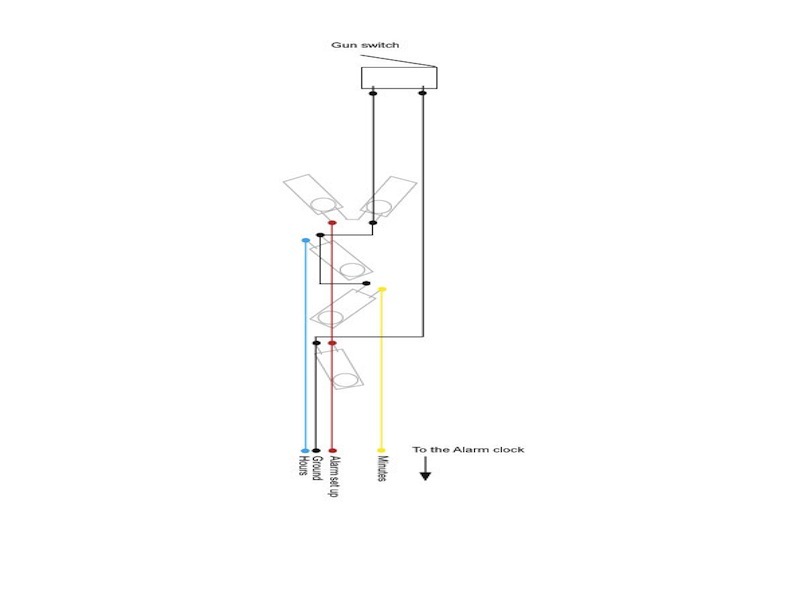
Locate the essential buttons’ contacts, 2 per button, and use a multimeter to follow each of them out to a solderable connection point. With the RC-70, all 3 buttons shared a common ground, so I needed to find a total of 4 connection points.
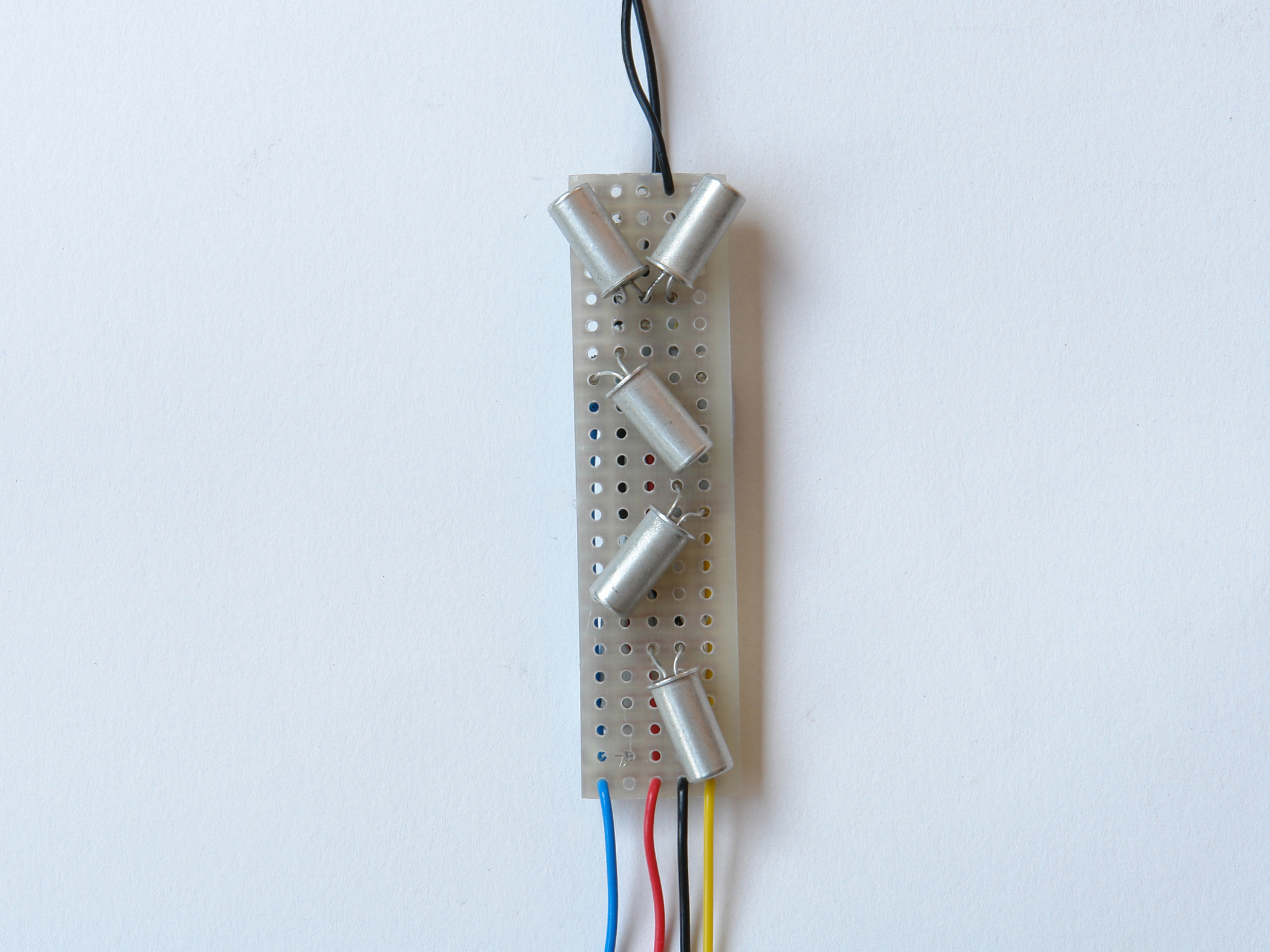
Solder wires from your cable to the contact points, using the color coding to track what goes where. Following convention, I connected the cable’s black wire to the shared ground, and designated colors for the 3 button-specific connections.
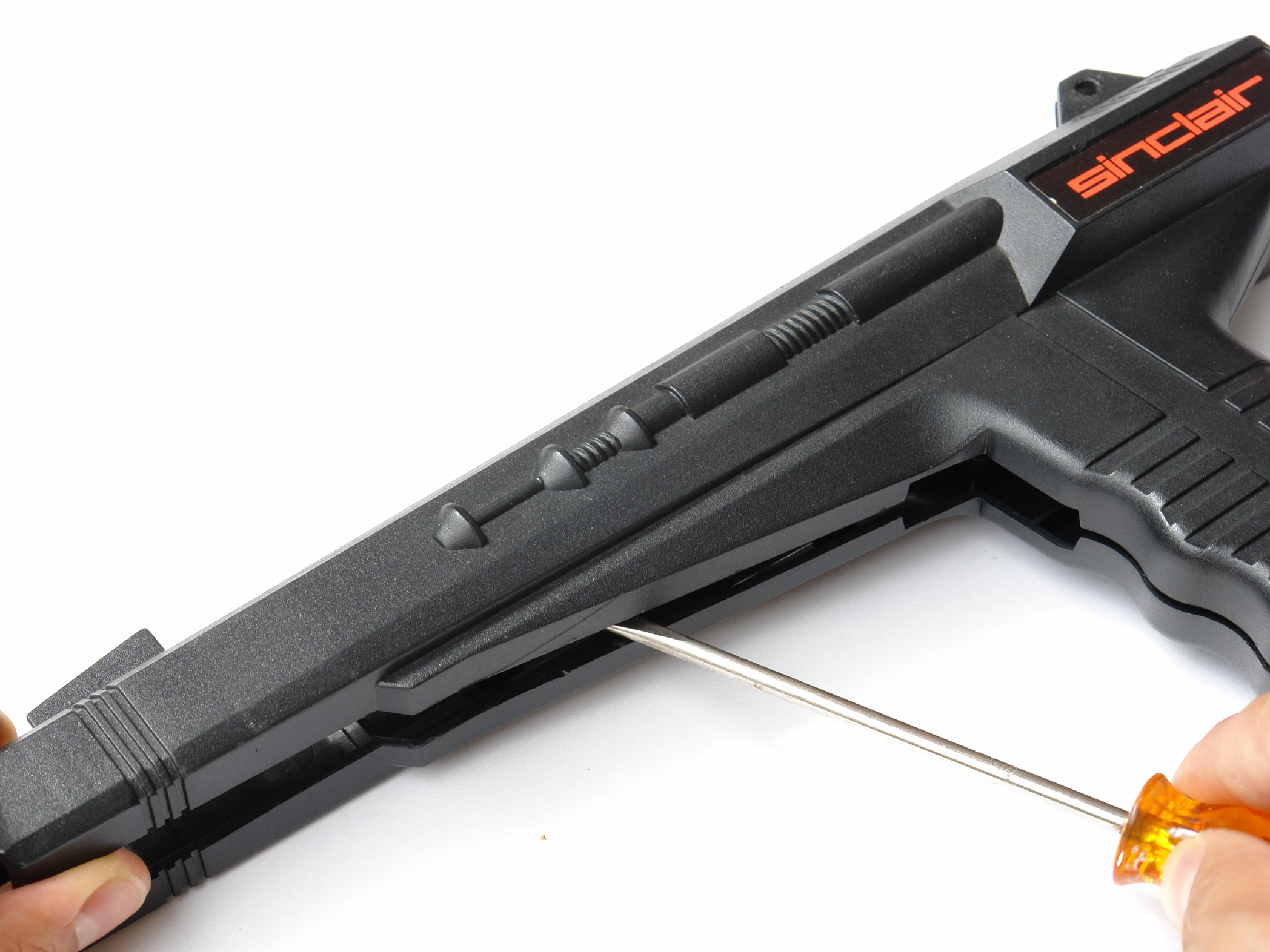
Organize and fix all the color cables between the free spaces of the clock. Trim extraneous cables to get them out of the way. Avoid placing cables near parts that get warm, such as the power converter.
Reassemble the clock and screw it back together.
Test the clock by plugging it in and touching together the other ends of the cable wires you just soldered. Confirm that bridging the wires mimics the functions of the buttons you connected them to. If you didn’t make any big mistakes, everything should work! Don’t worry about touching the wires with your fingers, because the current going through them is very low. Once it’s working, unplug it again.